By seamlessly integrating the physical and virtual worlds, spatial computing creates an immersive environment that enhances our perception, interaction and understanding of the digital realm.
In this blog, we will explore the transformative power of spatial computing in immersive Extended Reality (XR) experiences. We will also briefly see how leveraging Generative AI (GenAI) with spatial computing transforms and enhances XR experiences and elevates them to exciting new levels.
Spatial computing in XR
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR) and Mixed Reality (MR), providing users with immersive and interactive digital experiences. XR technologies have revolutionized the way we interact with the physical and digital worlds. Spatial computing refers to the convergence of multiple technologies, including computer vision, AR , MR , VR and advanced sensors as seen in Fig 1. to create an interactive and immersive digital environment that aligns with the physical world, enhancing XR for more intuitive, immersive and richer user experiences. It involves the mapping of digital information and virtual objects onto real-world spaces, allowing users to perceive, interact with and manipulate digital content as if it were physically present.
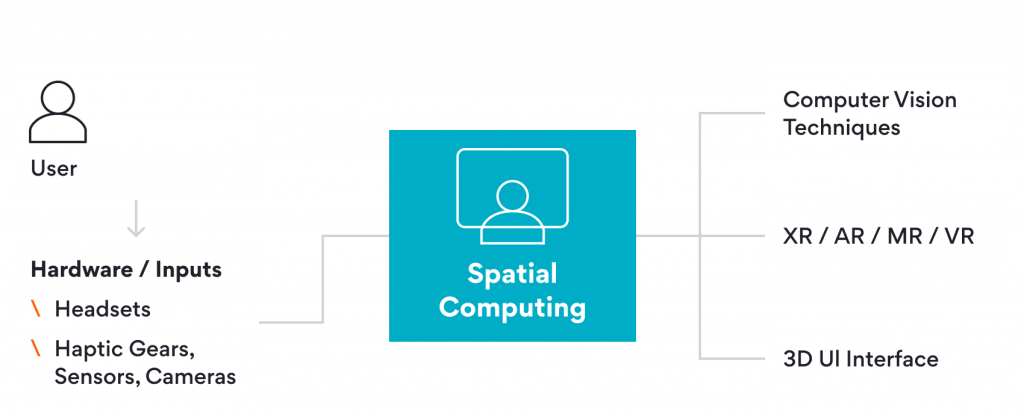
Spatial computing utilizes a combination of hardware and software components to enable seamless integration. It relies on Computer Vision algorithms and sensors to understand the user’s physical environment and track their movements and gestures. By accurately sensing the user’s position, orientation and interactions, spatial computing technology ensures that the virtual content aligns with and responds to the real-world context.
The goal of spatial computing is to enhance human-computer interaction by creating a more natural and intuitive interface.
How spatial computing significantly advances XR technologies
- Augmented Reality (AR): Spatial computing overlays digital content onto the real world and enhances a user’s perception of physical environments. It is essential in AR experiences as it utilizes sensors and spatial capabilities to accurately track a user’s position. It also helps augment digital objects in the real world, allowing for seamless integration and interaction.
- Virtual Reality (VR): By creating a virtual environment, spatial computing provides fully immersive and interactive experiences by helping to track and map a user’s movements and interactions within virtual environments.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Spatial computing combines AR and VR to blend the digital world with the real one by ensuring spatial presence and seamless user interactions, helping create compelling experiences.
Leveraging Generative AI with spatial computing to enhance XR experiences
Generative AI (GenAI) refers to a class of AI techniques that focus on generating different types of content, including text, images, audio, video, 3D models, etc., that are virtually indistinguishable from human-created content. GenAI models are designed to learn different patterns from data fed into them and utilize that knowledge to generate more intelligent digital data. (For a deeper dive on the intersection of GenAI and XR, read our previously published blogs on GenAI and NeRF)
By leveraging GenAI models in combination with spatial computing, businesses can contextualize digital information within physical spaces, enabling enhanced visualization, understanding and decision-making processes.
The fusion of Gen-AI and spatial computing is a transformative step forward in the evolution of building XR experiences, and it will lead to next-level XR Experiences in several ways:
- Contextual Experiences: Spatial computing enables the contextual understanding of data with the help of GenAI by mapping it to the real-world. This fosters a deeper comprehension of complex information, helping in decision-making processes across various industries like healthcare, manufacturing and many others.
- Enhanced, Personalized Immersion and Interactions XR experiences can be tailored in real-time to provide personalized content which enhances the immersion and interactions within the applications. Spatial computing enables users to interact with digital content, and GenAI models can provide inputs that lead to more authentic and intuitive interactions.
- Adaptive and Realistic Environments With the help of GenAI which can create highly realistic environments and characters, spatial computing enables users to interact, visualize and manipulate immersive environments, creating more adaptive XR experiences.
- Collaboration and Communication Spatial computing enables enhanced collaboration in ways previously never experienced with a merging of virtual and physical worlds. Traditional input methods are replaced by more intuitive and natural interfaces, and voice commands, eye-tracking and haptic feedback allows users to interact with digital content in a more natural way.
Apple Vision Pro – Apple’s First Spatial Computer
Several major vendors are working on bringing the power of spatial computing to the masses. Apple Vision Pro is the company’s first spatial computer that enables seamless blending of digital data and physical world. It operates by understanding and interpreting data using advanced computer vision algorithms and machine learning models and identifies surrounded objects, gestures and interactions, and responds accordingly. It enables users to interact with digital content using more natural and intuitive inputs — eye tracking, voice commands and gestures — eliminating the need for traditional controllers.
With visionOS, the world’s first spatial operating system, Apple Vision Pro lets users feel the immersion in their physical space while interacting with the digital content.
We will dive into the design and other aspects of Apple Vision Pro in a subsequent blog post.
Spatial computing use cases across industries
Spatial computing has numerous applications across various sectors, with massive potential to transform how healthcare, manufacturing, education organizations and others operate and deliver services. This can lead to enhanced productivity, streamlined processes, greater collaboration and improved user and customer satisfaction.
- Healthcare: The healthcare sector is already very active in its adoption of XR technologies in order to reshape patient care, medical visualizations and diagnostics by bridging the gap between the physical and digital realms. Leveraging spatial computing in XR experiences empowers patients to better understand their medical conditions by visualizing their own anatomy and treatment plans. This engagement enhances patient compliance, fosters informed decision-making and strengthens patient-provider relationships. Spatial computing also empowers medical professionals through XR experiences by allowing them to interact with 3D anatomical models and procedure simulations. This visual insight minimizes risks, enhances precision and shortens surgical times, resulting in safer and more
- Manufacturing: For XR experiences involving industrial simulations of various actions around machine workflows, spatial computing can help build more interactive experiences that accelerate the user’s understanding of those workflows and help in better retention of essential skills and knowledge.
- Data Visualization and Analytics: Spatial computing in XR empowers businesses from any industry to visualize and analyze complex datasets and information in a more intuitive way. By mapping real-time data onto the physical environment elements, businesses can gain deeper insights, identify patterns and make data-driven decisions.
- Remote Collaboration, Assistance, and Communication: Remote teams can better collaborate regardless of their physical locations by leveraging spatial computing in XR. By facilitating real-time communication and collaboration with this approach, companies can enhance productivity and reduce travel time and costs, as distributed teams can be connected in a virtual and interactive environment.
At Persistent, we believe in the spatial computing’s potential to impact enterprises and user experiences for significant business value. We have deep expertise in GenAI and XR applications and technologies, as well as experience in leveraging spatial computing to build various AR, VR and MR solutions. We help organizations identify the optimal XR technology for their respective enterprise use cases and build customized, intuitive and immersive experiences. We also provide consulting, design, development and ongoing support services to our clients. For more information about our XR offerings, reach out to us.






